You May Not Know Wayne Kady, but You Know the Cadillacs He Drew
Wayne Kady might be the most well-known unknown designer in the history of General Motors. Well known, because his designs are some of the most recognizable from the 1960s to the 1990s; unknown, because the unassuming Kady was often eclipsed by flashier designers more adept at self-promotion.
Kady’s tenure at GM began in 1961, when the General was at the zenith of its influence—so all-powerful that the government considered taking action to break up the automaker’s near 50 percent grip on the American market. GM Design was the undisputed leader of automotive styling, and Kady was in the thick of it, working for legends like Bill Mitchell. He soon landed at the studio where he made the most impact—Cadillac, where he penned the 1971 Eldorado and helped steer the brand through the vehicle downsizing of the late ’70s. By the time he retired in 1999 as chief designer, Buick 2 Studio, his portfolio contained some of the most recognizable cars to come out of Detroit.
Over the course of many interviews, Kady told us his story, which is also the story of how one person can make a huge impact on an industry and a culture.
California beginnings

I grew up in Reedley, California, a small farming town located in the heart of the San Joaquin Valley. My dad immigrated here from Lebanon and saved up enough to buy a small farm. My first experience driving was on our tractor. Dad had a ’29 Chevrolet truck that was no longer used and was going to be scrapped, so Dad let my brothers and me take it apart. I learned about how an engine works and how to turn a wrench, as well as how to skin my knuckles. By the eighth grade, I could draw all the GM cars from memory. In my junior year of high school, I bought a 1940 Willys for $12 and started to build a sports custom. My inspiration was the Jaguar XK 120. I never finished it, but I learned how to weld and graft sheetmetal—and how to use a lot of Bondo. What inspired me to become a car designer was I learned that you could earn a living doing it. In January 1951, Life magazine published photos of the Le Sabre show car. It was an inspiring thing to see, that “Wow, all of a sudden, it’s the future!”
ArtCenter
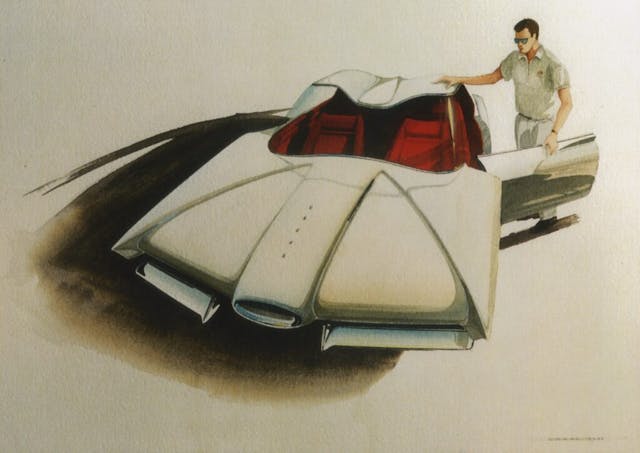
In high school, my art instructor saw me drawing cars when I should have been drawing other things. He told me about ArtCenter College of Design [located in Los Angeles, California, before it moved to its present location in Pasadena] and suggested I apply. I did, and they rejected me. They said I was too immature. After two years at Reedley Junior College and a second attempt for admission, they let me in on probation.
Hired by General Motors
Clare MacKichan, the chief designer of the ’55 through ’57 Chevrolets, came to ArtCenter and interviewed me and several other students, shortly before I graduated with honors. He looked at my portfolio and offered me a job. I moved to Detroit on February 13, 1961. The farthest east I’d ever been was Phoenix, Arizona. That was the first time I’d ever flown. I had a window seat and I was looking out as we were circling Willow Run Airport. I couldn’t see anything moving, and everything was white. I sat there wondering what I was doing. I got off the plane and had to walk across the tarmac because Willow Run didn’t have jetways back then. I didn’t have an overcoat, just a suit coat. When they opened the door, it felt like nails going through you, it was so cold. My first night in Michigan was spent sleeping on the floor of Syd Mead’s apartment in Royal Oak. Syd was a fellow ArtCenter graduate and legendary designer who went on to create designs for the Blade Runner and Tron films.
It sounds like a cliché, but my first day at GM, I couldn’t believe that I was hired to work at this place. It was an environment where you couldn’t wait to get to work, because if that’s your passion, that’s the ideal place to be. The environment was such that you wanted to be as creative as you could be, the ideas had to flow out, and you had to be competitive with whomever else was working there, too. Working at GM back then was fantastic. It was a very creative environment to be in.

Bill Mitchell
I first met Bill Mitchell when I was newly hired and assigned to Design Development, the studio where all newly hired designers started. There they could be evaluated, then assigned to a studio where they could be most effective. I remember whenever Mitchell would visit the studio, he was always dressed in expensive, tailored suits and had someone with him taking notes. Later, after I was assigned to Cadillac, Mitchell would visit the studios to check on the progress of the clay models. If he wasn’t happy with the direction the design was headed and you tried to defend it, his face turned red, and you knew a chewing out would follow. Usually he would come back after a couple of hours knowing everyone was tense and uptight, and then he would tell a joke or make an off-color comment and then walk out, and that would lighten the air. Some designers had a hard time with him, but I thought he was very effective. He might have been a little crude in some areas, but he was successful as far as picking the designs for production.
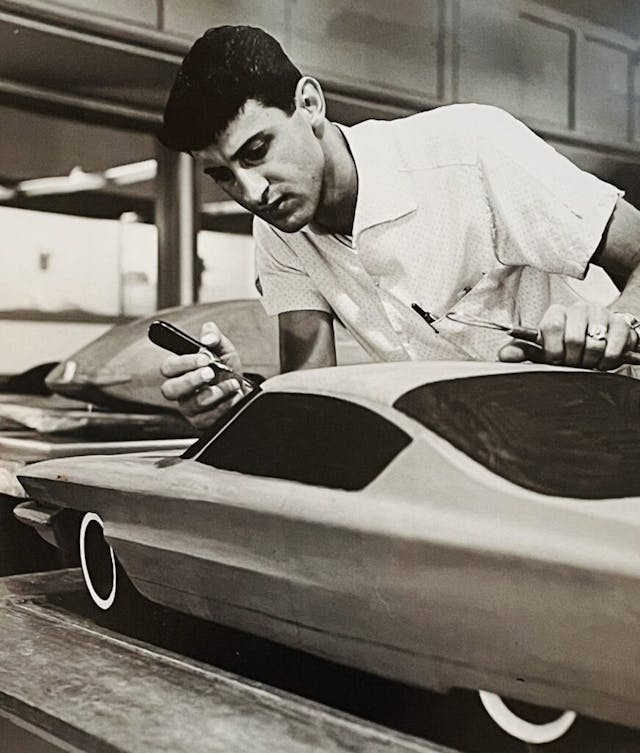

Designing at Cadillac
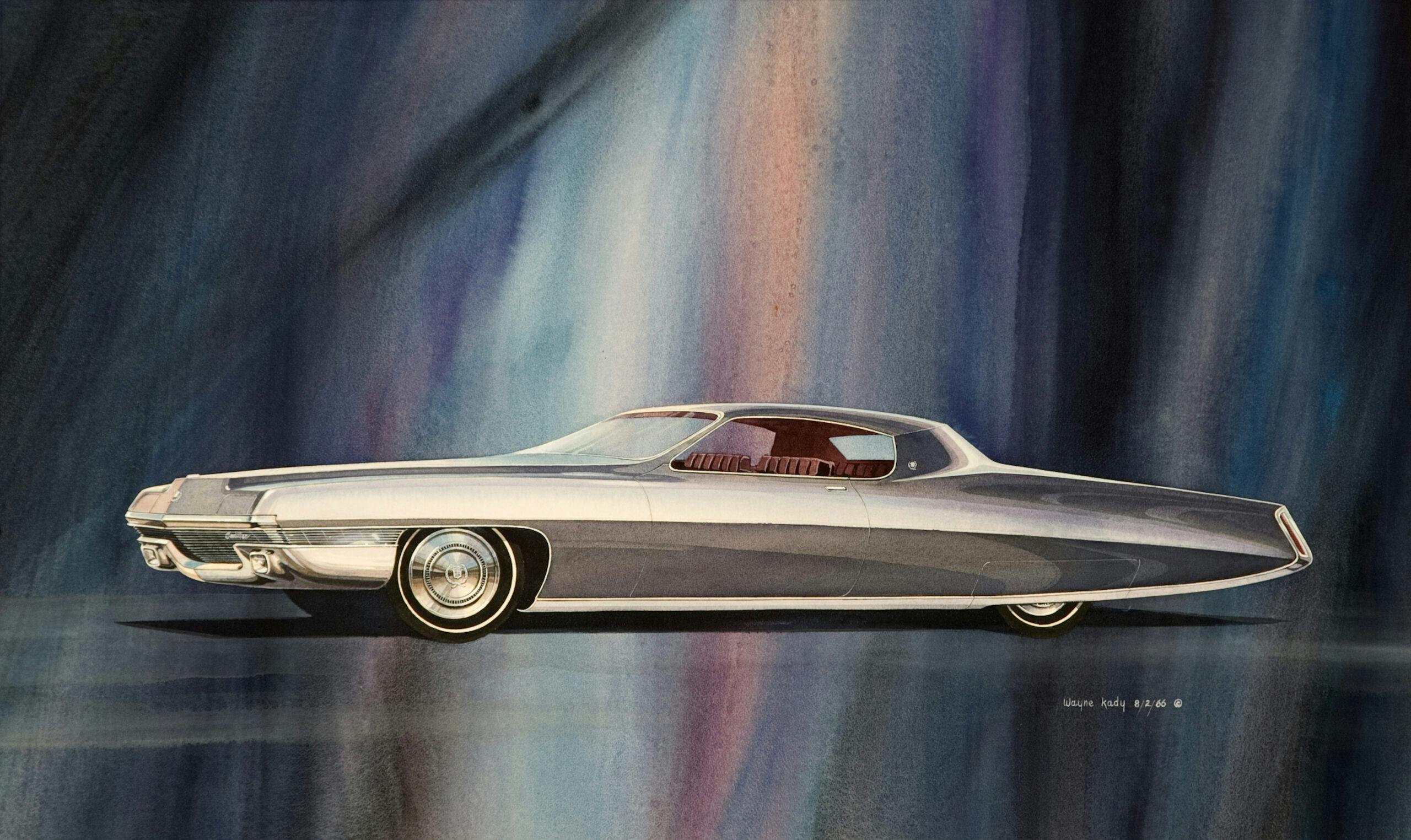
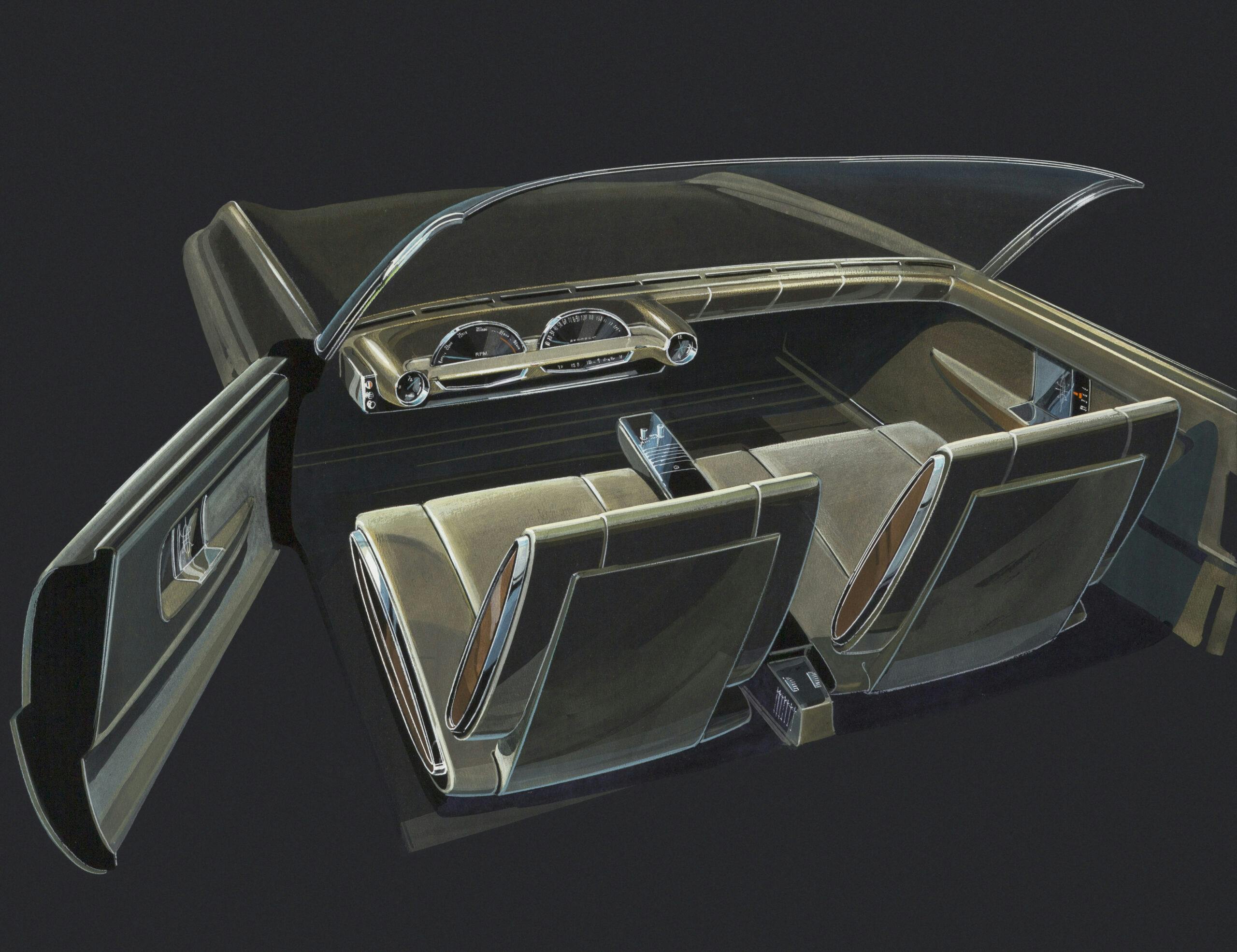
In 1962, while assigned to Bernie Smith’s Preliminary Design studio, our project was to create an alternate design for the 1965 all-new Cadillac versus the direction the Cadillac studio was pursuing. Smith’s theme was chosen, and I was transferred to the production studio to help design the ’65 DeVille and Fleetwood. We were also working on a theme that eventually led to the design of the ’67 Eldorado. In August 1968, I was promoted to chief designer of a newly formed advanced Cadillac studio to design an all-new Eldorado for 1971.
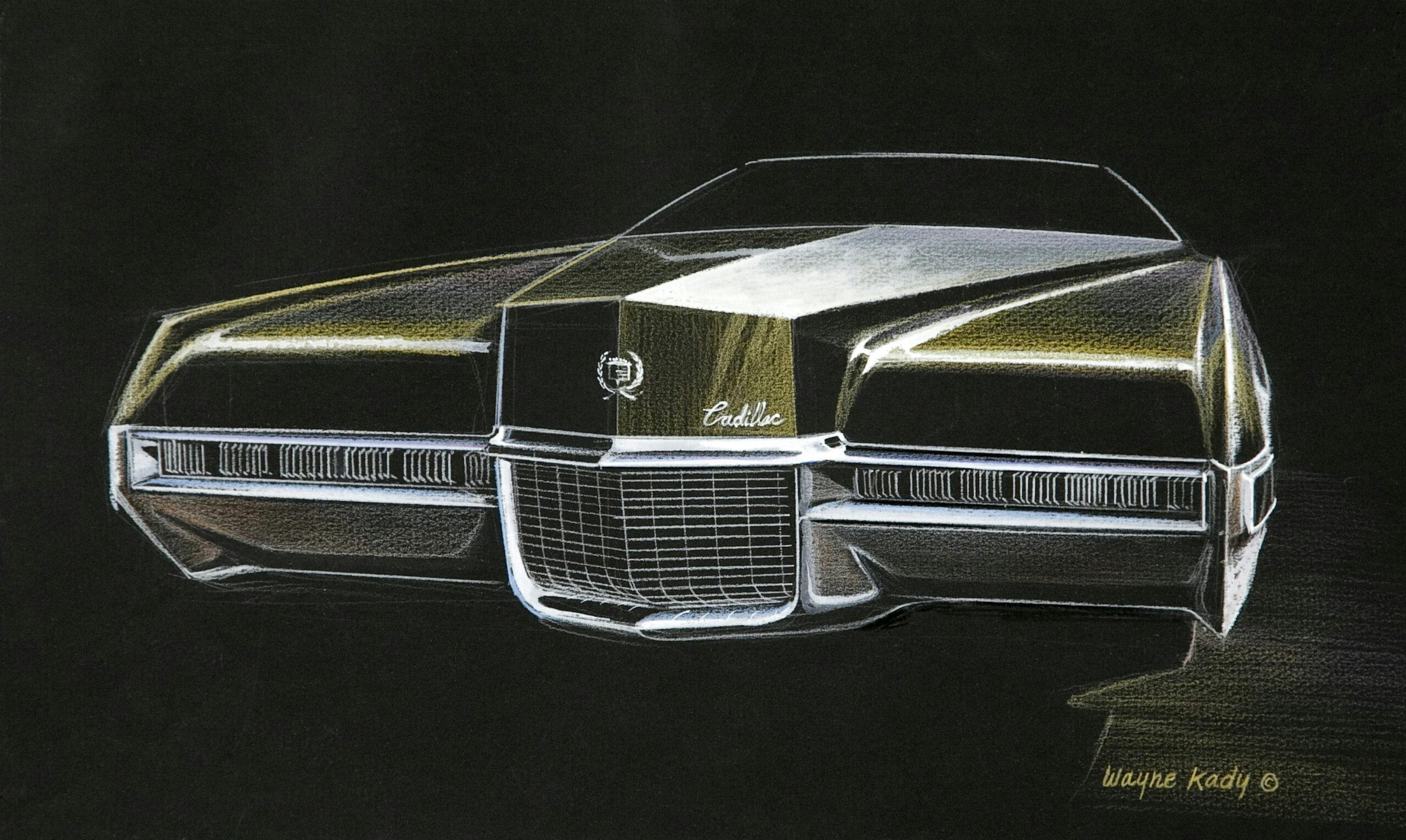
1971 Eldorado
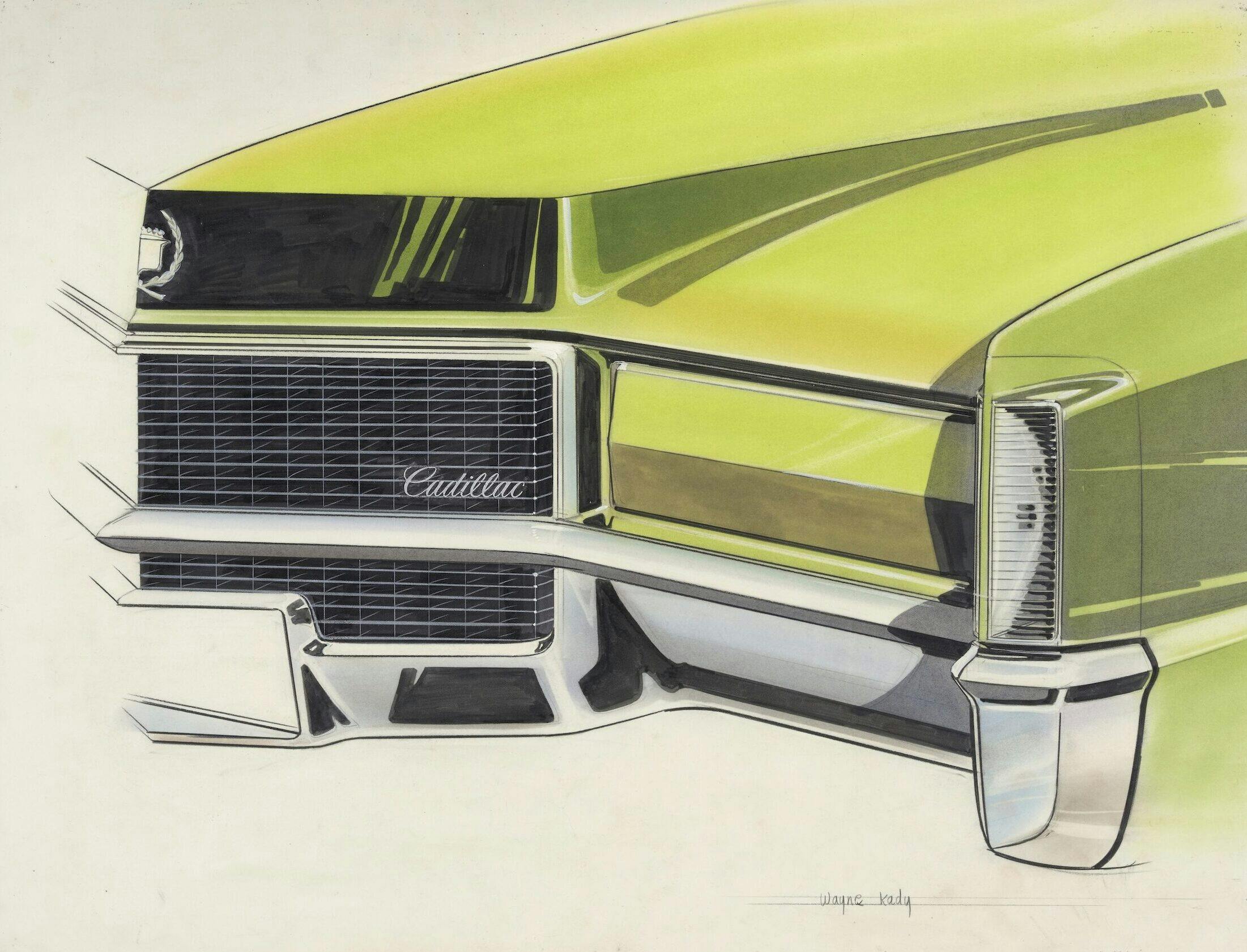
The ’67 Eldorado, [Oldsmobile] Toronado, and [Buick] Riviera were designs initially developed with unique sheetmetal for each brand. Cowl, windshield, and side-glass planes were the only major parts shared. Eldorado shared front-wheel drive with Toronado, while Riviera continued with rear-wheel drive to enjoy a price advantage as well as differentiation. When I was working on the Eldorado for 1971, we started out with a smaller, more tailored body. As the design progressed and volume cost estimates and other data evolved, we ended up having to share the B-body platform used by all five car divisions and even sharing the roof panels between Toronado and Eldorado.
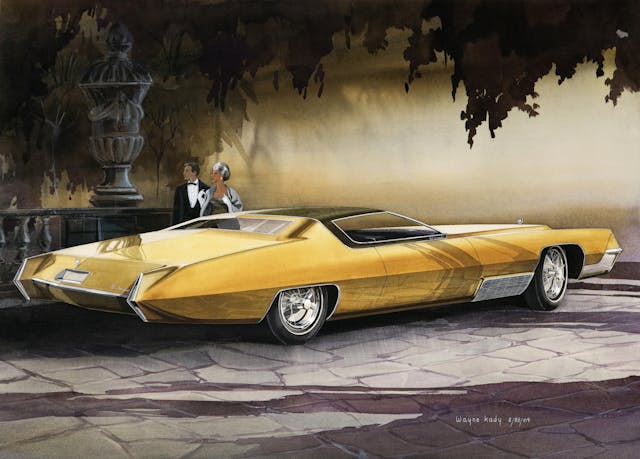

The ’67 was a big act to follow, because the car was, as far as designers are concerned, probably the best-looking Cadillac for a long time. The 1967 through ’70 Eldorado had a two-piece hood. When they’re stamped in two pieces, they’re assembled to the center and then the ends have to be welded and metal finished. Metal finishing cost a dollar an inch back then, and the ’71 hood required 9 inches of welding and metal finishing, so it cost $9 per car. In those days, if you took 50 cents out of a car, that was big money. Wally Sitarsky was the die engineer at Cadillac; I had great respect for him.

After careful study, he found a way to make the hood of the 1971 Eldorado in one piece. [This technique saved Cadillac almost $250,000 in 1971, roughly $1.8 million in today’s dollars.] Another important cost savings for Cadillac was sharing the front-center bumper and guards with the DeVille and the Fleetwood series.
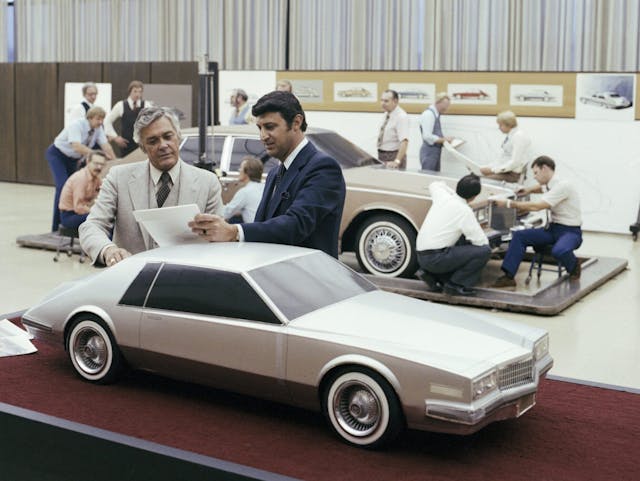
1976 Seville, Part 1
After completing the design on the ’71 Eldorado, we had a fiberglass model built of a four-door DeVille concept with horizontal taillights before starting work on a small Cadillac to compete against the Mercedes 280SEL. We had completed a set of renderings of three possible approaches: importing the Opel Diplomat [Opel was GM’s German division], importing an Opel with minor changes to the front and rear, or creating an all-new car. These were taken by the sales team and the general manager to dealer councils across the country, where they were evaluated and voted on as to whether we would even have a smaller Cadillac. Cadillac was having competition on the West Coast in particular with the Mercedes. As that project started to roll, I got transferred to Buick. Mitchell called me into his office, and he didn’t really say much. He just said, “Hey, kid. I’m transferring you to Buick. They got a problem in there. Get out and fix it.” He used to call me kid. I was pretty young then.

Buick
One of the reasons that I was sent to Buick was because Mitchell was pressured to change the boattail Riviera. The Buick general manager disliked it and thought it was too controversial. Mitchell wanted me to graft the design that came off the four-door Cadillac with horizontal taillights onto the back of the boattail Riviera. The doors had to be kept, while the roof panel was shared with the Toronado and Eldorado. We also had to incorporate the new 5-mph bumper standards. We didn’t have enough money to change a lot on that car except maybe the quarter-panels and the decklid and add high-level brake lamps. I managed to make it look more conventional, which satisfied Buick. It didn’t enhance the look and did not add sales. I always thought the boattail was better-looking. Mitchell’s the guy who pushed the design of the boattail Riviera, but Jerry Hirshberg was the chief designer. After [facelifting] the LeSabre, the Electra 225, and a major facelift to the ’76 Buick Regal series, I was transferred back to Cadillac as exterior chief designer.
1976 Seville, Part 2

Back at Cadillac, I reinherited the Seville that was marketed as a ’76 model; its design was already finished when I returned. The design was done by Stan Parker, my first boss at Cadillac. It was a big hit for the division, and it answered the competitive question to the Mercedes. It introduced Cadillac into that small-car segment, at a big price. I think it was priced higher than anything except for the limousine. [1976 Cadillac Seville MSRP was $12,749.] From my perspective, it was the proportions that made the design so successful. One of my colleagues once mentioned proportions as being to design as location is to real estate. I think anytime you start a design for a car or a house or a product, proportions are one of the first things that you want to address. When I’m talking about proportions, it’s the dash to axle, the location of the front wheel in relation to the windshield, the amount of overhang in front of that wheel, and then the location of the rear axle to the roof profile. Then the placement of the wheels to the width of the car. These are all the things that you see while you’re looking at a car, whether it’s moving or static. The Seville’s A-pillar looks swept back, but that’s more dramatic because the roof profile was so upright and formal.
Earlier in my Cadillac career, somebody had taken a survey of our owners’ garages, and a lot of them had garages that were attached to older houses. The houses might have been big, but the garages weren’t, because nobody anticipated cars growing to that length. We got to a certain length, and we were told, “Don’t go any further because we’re going to lose customers.”
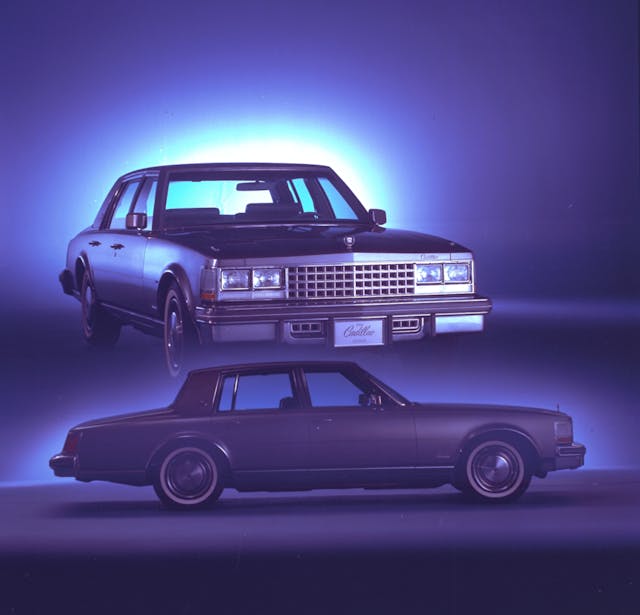
Downsizing at Cadillac
The first major downsizing project was the ’77 DeVille and Fleetwood. I’d started a little of that [downsizing] at Buick before I left. I think the assignment was to get a thousand pounds out of the car, so we had to reduce the size. Part of the assignment was to make the car look more fuel-efficient. We had these large cars that looked irresponsible and were getting maybe 12 mpg, then we’ve got Asian cars that are getting 25 [mpg] or more. That’s what people were concerned about back then. Even if the car got good fuel economy, it was the image that was part of the reason for downsizing. There were people at Cadillac who were talking about the bulk of the car and the appearance that we were wasting the nation’s resources and that we were greedy.
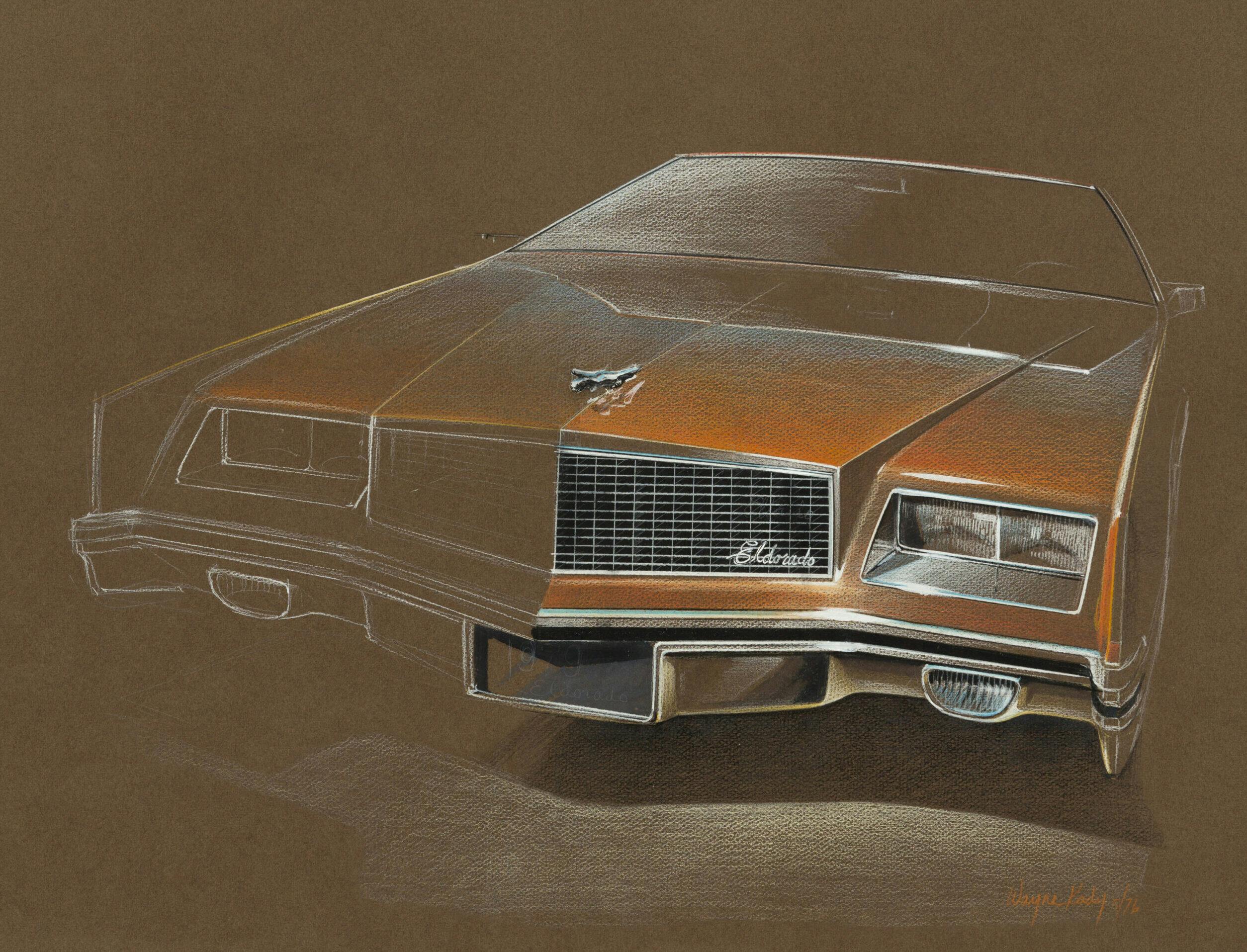
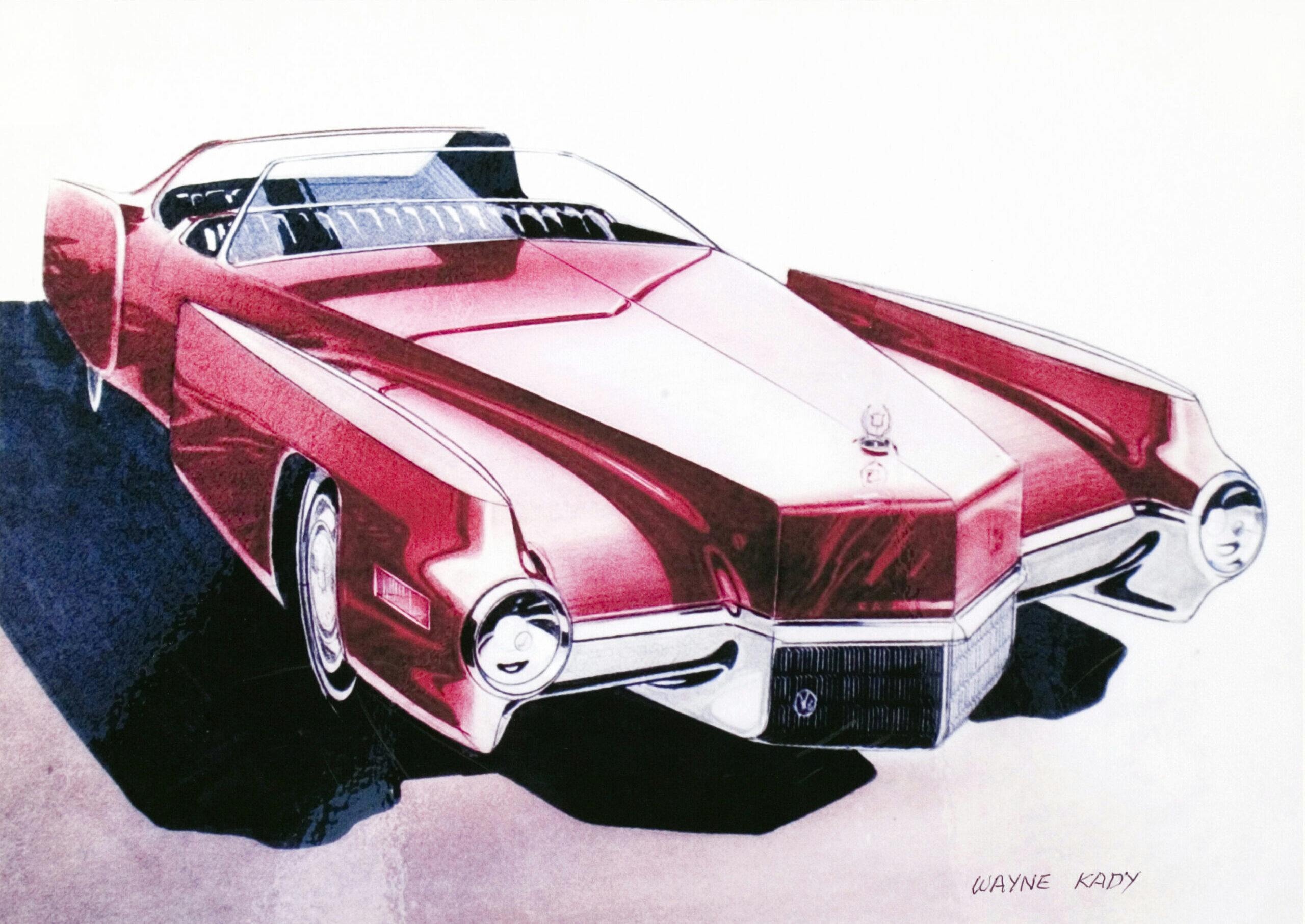
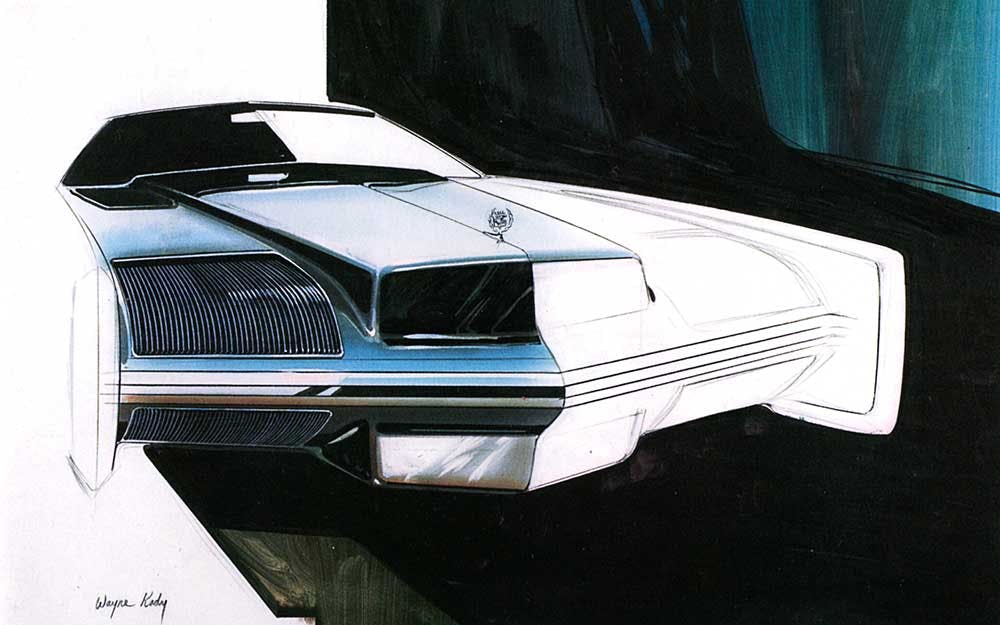
1980 Cadillac “Bustleback” Seville

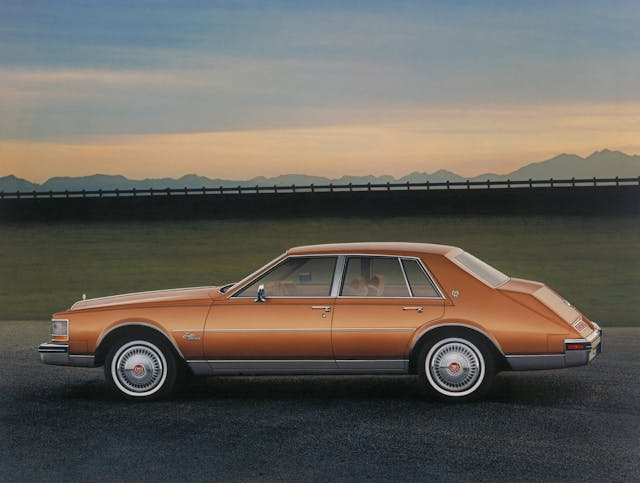
After we finished the design of the ’67 Eldorado, we were given time to sketch whatever we wanted, and we were putting together advance concepts. I always had an interest in something that was unique and a little different for the rear of the car. Harley Earl used to say, “The most important part of a car design is the front end.” But I thought maybe the rear end was just as important.
Tailfins had run their course, and it occurred to me that people spent a lot of time looking at the back of a car. I thought, “There’s an opportunity to make a car distinctive and different.” I had been sketching that idea since probably the early to mid-’60s. We were looking at this design for the ’79 Eldorado, and we’d shown the clay model to Ed Kennard, who was the general manager of Cadillac. He rejected it and Bill Mitchell asked if he’d consider it for Seville. Kennard said he would look at it, and I think he was placating Bill for having rejected it outright as an Eldorado. We added another door cutline and that’s how it became a Seville. I was invited to the dealer announcement in Long Beach. When they announced that car, they had it on the stage and when they pulled the curtains back, the car started to revolve on a turntable and was partially concealed with fog. Then the lights gradually came on, like the sun coming up. As the fog cleared, you could see the car. It got a standing ovation. I’ve been to a lot of these dealer announcements, and this was by far the most applause for a new car that I’d ever seen. But then they priced it, I think, almost $4000 more than the previous year. They added a lot of standard features, like a diesel engine. Those engines were extremely problematic and added to the car’s price. I remember going into a dealer showroom and people would walk up to that car, they’d look at the sticker price, and then they’d look at an Eldorado or DeVille and many of them would go for the less expensive option. Then they had the V-8-6-4 [GM’s first attempt at cylinder deactivation] and the technology wasn’t ready. The electronics weren’t worked out, and the dealers didn’t know how to fix it—the factory didn’t have a fix. It was a time when fuel economy was a huge problem, and the corporation was doing all it could to squeeze out as many miles per gallon as possible. I’d give credit to Cadillac engineering for advanced thinking and having the fortitude to produce it. It’s just too bad that the technology wasn’t proven. They were ahead of their time. Today cylinder deactivation is standard on a number of cars.

I remember being at a dealer council meeting and the dealers were very upset with the general manager and the chief engineer. I think I was included in the meeting because the Seville was controversial with that bustleback and I would share some of the criticism. Oh, they were very upset. One of them was Don Massey [known as “the Cadillac King,” at his peak, Massey was one of the largest Cadillac retailers in the country, accounting for approximately 6 percent of the brand’s sales], but he was fairly cool. The one who was the most vocal and angry was John DeLorean’s brother, Charles, who owned a Cadillac dealership outside of Cleveland. Another dealer belonged to the same country club as some of his customers, where he would regularly overhear one of them asking another member how they liked their new Cadillac. The other member responded, saying, “I hate it. It’s been at the dealership, and he can’t find a fix for the engine.” And DeLorean says to us, “I’m losing my customers, I’m going to lose my franchise, and it’s because of you SOBs.” They were literally calling the general manager and the chief engineer SOBs right to their faces. It was pretty nasty. Massey was the last to speak. He looked at Kennard, and he said, “Well, boss, looks like we got work to do.”
The Cadillac Allanté
The 1989 model year was my last year at Cadillac. One of my final projects was an alternate design to the Allanté. I was not happy when I found out that Bob Burger, Cadillac’s new general manager, was going to [Italian design house] Pininfarina to build a two-passenger car. I asked Burger, “How is it that we can do your bread-and-butter products, but then when it comes to a fun and historic project, you give it to somebody who hasn’t done anything for you?” He answered, “Well, this is business. We want that designer label.” I said, “What do you mean, ‘designer label?’” He said, “We want a designer label on the car, like the red tags on the back of Levi’s.” I asked him, “What do you think we are?” He replied, “Nobody knows who you are.” And he was right. Nobody knew who we were. Bill Mitchell received credit for everything, but the designers, they were unknown to the public. We put together an alternate version of the Allanté anyway. It wasn’t any better than what I think Pininfarina came up with, but we had to do something to keep the team together. The morale was shot when they found out about it. I think if Mitchell had still been there, he probably would have fought Burger on that one.
Back at Buick
I was transferred to Buick after the ’89 model year. I shared responsibility for Buick exterior design with Bill Porter [another design legend at GM, who was responsible for the 1968 Pontiac LeMans/GTO, the 1970 Pontiac Firebird, and the 1982 Chevrolet Camaro/Pontiac Firebird, among others]. Bill was leading the design for the LeSabre, the Park Avenue, and the Riviera. I was responsible for the Century, the Regal, the Skylark, and the Roadmaster, which was based on the same platform as the Chevy Impala; the estate wagon version of it was done by my assistant, Dennis Wright. He brought back woodgrain trim on the sides of the car, and some of the designers disagreed. Dennis told me at one time, he thought that the Roadmaster estate wagon outsold the Impala version. We were there to design cars to sell for profit. That’s what we were paid to do.
I retired on April 1, 1999, after a little over 38 years at General Motors. Coming from a farm, as a farm kid, I never would’ve dreamt that I would have been working at General Motors from day one. And to work on Cadillac, on GM’s top brand, and be the chief designer longer than anybody else in the history of Cadillac. I made a good living, met a lot of great people, and worked with some of the most talented people in the world for automobile design. You know, what’s there not to like?
***
Check out the Hagerty Media homepage so you don’t miss a single story, or better yet, bookmark it. To get our best stories delivered right to your inbox, subscribe to our newsletters.


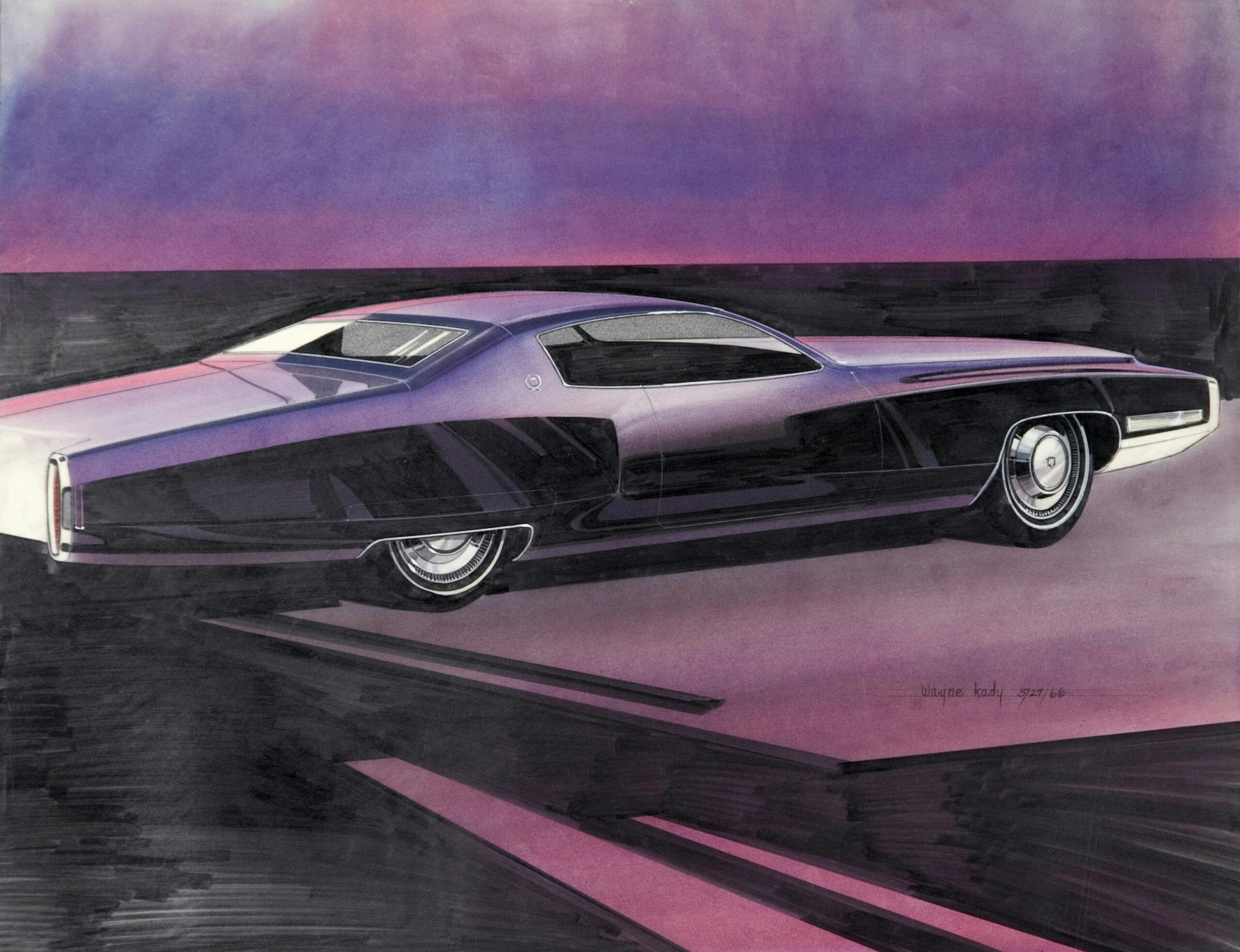





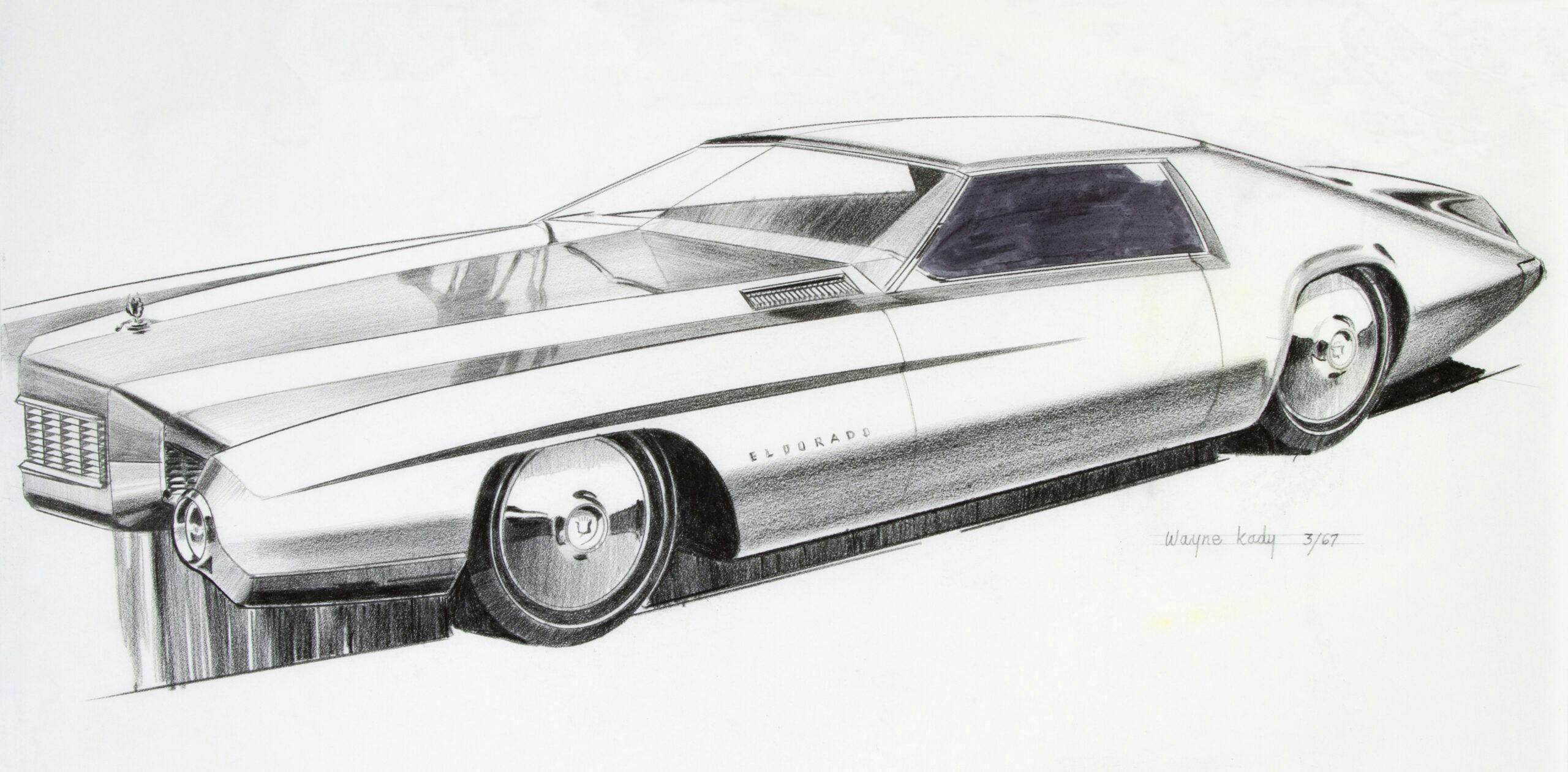
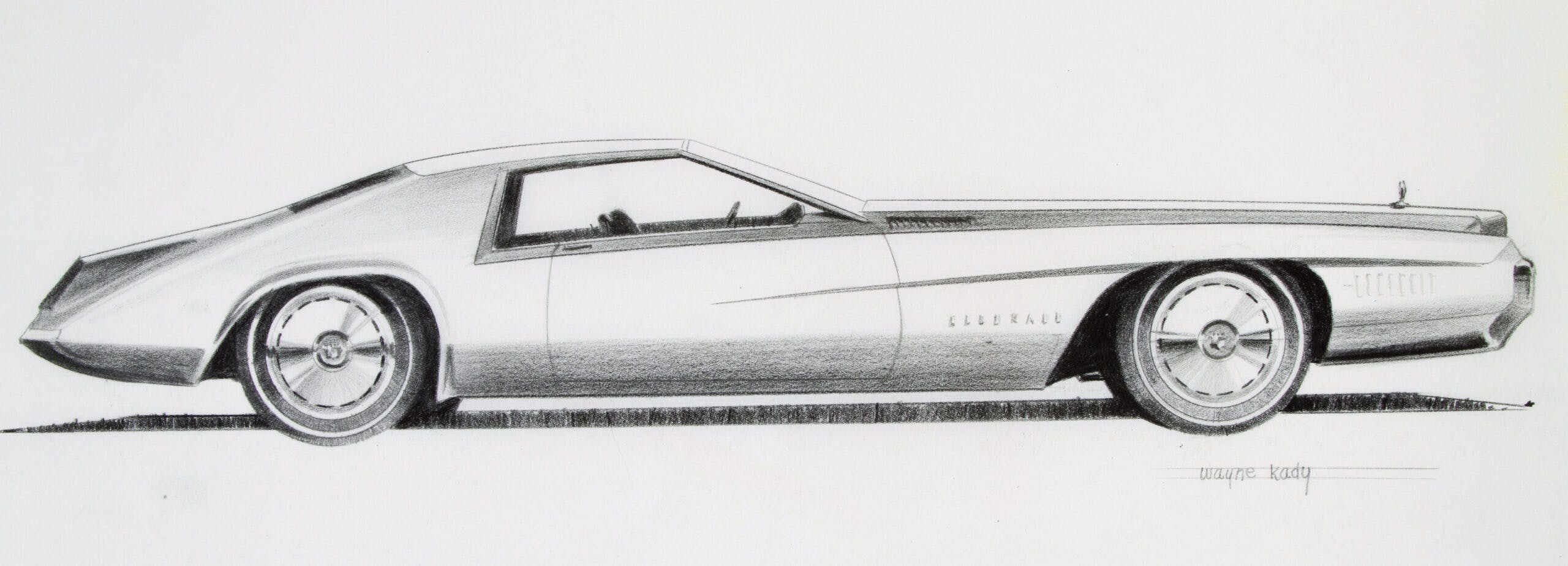





To be fair Bill was working in a very difficult era. I feel he came late for his styles. I think in the 30’s he would have been a top designer.
But the cars he did most were controversial and or just not well remembered. The bustle back Caddy is a cult favorite mostly for being odd.
I did feel his best was the first Seville.
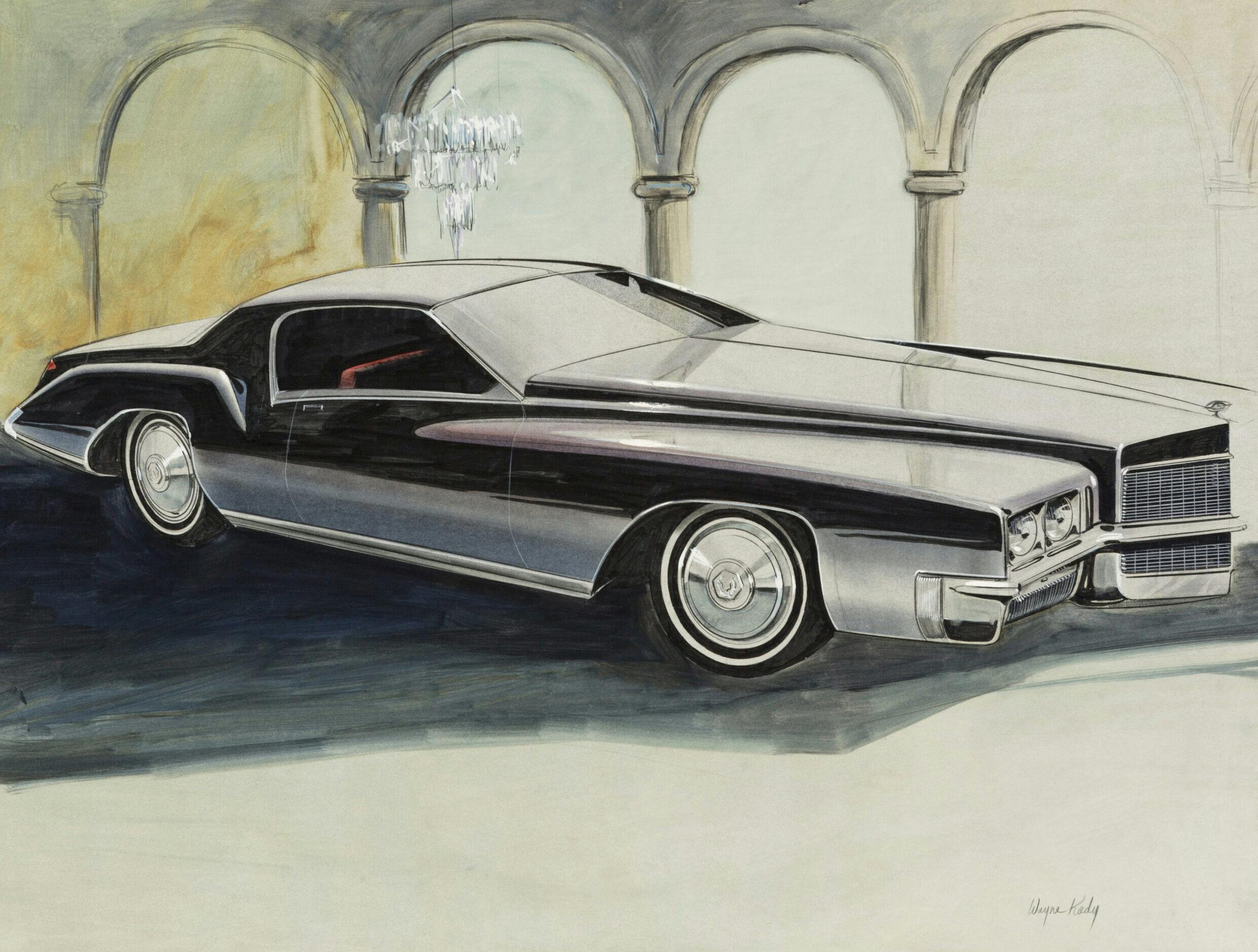
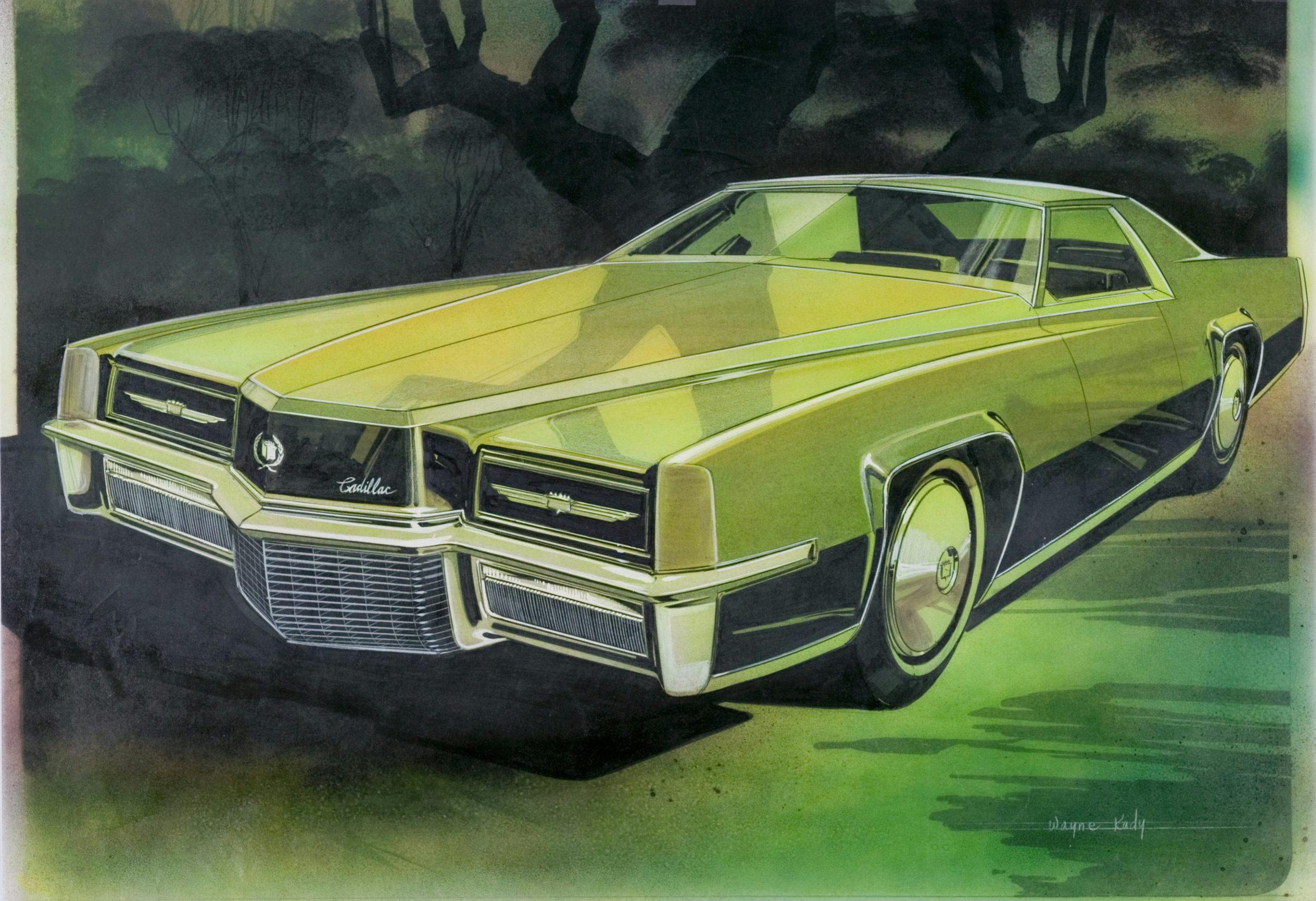
The 67 Eldo drawing in Gray shows hints of his work at Buick and the Purple one really has a 1970 Monte Carlo look.
The 70’s and 80’s were not the best for styling
He wasn’t responsible for the original Seville. The article states he was at Cadillac when concepts for a new smaller Cadillac were being evaluated. He left for Buick and came back to Cadillac after it was designed. Stan Parker was the designer.
I disliked the bustle back Seville but I hated the ubiquitous use of the formal upright backlight on almost every GM model into the 80’s, especially on coupes
I want to share some drawings to consider
You all may recall that in the same year or two of the Caddy bustle back, both Lincoln and Imperial had bustle backs. Also years later the big BMW sedans had a bustle back.
What is really mph kpm this cady can furlong when gaurantee ? a 2015 cady is still for road use .?in that years now 2023 cady,s is at lesser rated cars now ? But it is turn out to be used cars and offers.
’70’s / 80’s is not the glory days of Cadillac. As the cars lost power, etc. so does my interest go down. It took the CTS-V to get me interested in Cadillac again.
Give me 1962 de ville or 1967 el dorado best styles ever, the rest of the Cadillacs you can have However, I did have a 69 el dorado and my 72 Audi 100ls would run circles around the caddy, out accelerate it, got 3 times more mpg and had plenty of interior room and comfort, was also very clean simple looking, needless to say I dumped the caddy and never looked at another one.
Cadillac hit its prime with the Worlds Fair V16 coupe in the 30’s. That car was back when they really were still the standard of the world.
GM got greedy and should have left the Cadillac only to the high end buyers and not made it for everyone. That was what Buick was for. Cadillac became a rebodied Buick.
Then in the 80’s when the market went to BMW and Benz sport sedans they went to a FWD down sized car with a hand granda engine.
Today the V Series is doing well and more people are waking up to it but this is at a time where ICE performance is going to go away with Government regs. The hot rod community is really embracing them.
I always thought that the the “bustle back” Cadillacs were very austere. That was in direct conflict with all the chrome and doodads on the front. I wonder how a Seville with a “coffin nose” like the mid 30s Cords have would have tied the design together. Maybe that’s why I’m not a car designer